ⅰ. ما هو حمض الفورميك؟ من الخصائص الفيزيائية إلى الخصائص الكيميائية
حمض الفورميك، المعروف بشكل شائع باسم حمض الميثانويك، هو أبسط الأحماض الكربوكسيلية ذات الصيغة الكيميائية HCOOH. وهو سائل عديم اللون وينبعث منه دخان برائحة نفاذة، ويُوجد في إفرازات النمل والدبابير واليرقات.
الخصائص الفيزيوكيميائية الأساسية لحمض الفورميك:
نقطة الانصهار: 8.2-8.4°م
نقطة الغليان: 100-101°م
الكثافة: 1.22 غ/مل (عند 25°م)
الحمضية: أقوى من باقي الأحماض الكربوكسيلية في سلسلته المتجانسة، لأن مجموعته الكربوكسилية مرتبطة مباشرة بذرة هيدروجين.
الخصائص الفريدة: يُظهر خصائص مزدوجة كحمض والدهيد، مما يمنحه خصائص حمضية وخصائص اختزال.
إن الحموضة القوية وطبيعة حمض الفورميك المختزلة تجعلانه ذو قيمة عالية لمجموعة واسعة من التطبيقات الصناعية، ما يجعله مادة كيميائية لا غنى عنها في العديد من العمليات الصناعية.
ثانيًا. طرق إنتاج حمض الفورميك: من العمليات التقليدية إلى التكنولوجيا الحديثة
لقد مرت طرق الإنتاج الصناعي لحمض الفورميك بعدة ابتكارات تكنولوجية. حاليًا، تُستخدم الطرق التالية بشكل رئيسي:
1. طريقة فورمات الميثيل: تُعد هذه الطريقة حاليًا الأكثر شيوعًا لإنتاج حمض الفورميك. في هذه العملية، يتفاعل أول أكسيد الكربون أولاً مع الميثانول ليشكل فورمات الميثيل. ثم يتم تحلل فورمات الميثيل مائيًا تحت تأثير عامل حفاز حمضي لإنتاج حمض الفورميك. تُعتبر هذه الطريقة متقدمة تقنيًا وقابلة من الناحية الاقتصادية، ما جعلها العملية السائدة عالميًا.
2. طريقة فورمات الصوديوم: هذه طريقة أكثر تقليدية. يتفاعل أول أكسيد الكربون مع هيدروكسيد الصوديوم تحت درجة حرارة وضغط عاليين لإنتاج فورمات الصوديوم، والذي يُعامل بعد ذلك بحمض الكبريتيك للحصول على حمض الفورميك. هذه الطريقة تستهلك مواد وطاقة نسبيًا بكثافة عالية، ولكنها لا تزال تُستخدم في بعض التطبيقات.
3. طريقة الفورماميد: باستخدام ميثوكسيد الصوديوم كمحفز، يُمرَّر أول أكسيد الكربون عبر محلول ميثانول الأمونيا لإنتاج الفورماميد. يُحلَّل الفورماميد بعد ذلك بحمض الكبريتيك للحصول على حمض الفورميك.
بفضل التطورات التكنولوجية، أصبحت طريقة ميثيل فورمات هي العملية المفضلة نظرًا لفعاليتها العالية وفوائدها الاقتصادية، مما يسهم في النمو السريع لصناعة حمض الفورميك.
التقنية المتقدمة لإنتاج حمض الفورميك: الريادة التكنولوجية تعني الريادة في السوق
طريقة ميثيل فورمات: العملية السائدة عالميًا
تُعد طريقة فورمات الميثيل حاليًا الأكثر انتشارًا وتطورًا في عمليات الإنتاج على مستوى العالم، حيث تمثل أكثر من 80٪ من إجمالي إنتاج حمض الفورميك. وتتميّز هذه الطريقة بمزايا شاملة من حيث النضج التكنولوجي، والكفاءة الاقتصادية، واستقرار جودة المنتج. وتشمل مزاياها الأساسية ما يلي:
● استخدام عالٍ للمواد الخام، مما يؤدي إلى تكاليف إنتاج أقل بنسبة 25-30٪ مقارنةً بالعمليات التقليدية.
● جودة منتج مستقرة، قادرة على تلبية متطلبات القطاعات التطبيقية الراقية.
● صديقة للبيئة، وتقلل انبعاثات مياه الصرف والغازات العادمة بأكثر من 50٪.
● مرونة تشغيلية كبيرة، تسمح بتعديل السعة الإنتاجية بسرعة وفقًا لطلب السوق.
مقارنة التكنولوجيا: لماذا تختار العملية المتقدمة؟
بالمقارنة مع الطريقة التقليدية باستخدام فورمات الصوديوم، تُظهر عملية فورمات الميثيل المتقدمة مزايا واضحة عبر عدة أبعاد:
● تقليل استهلاك الطاقة: ينخفض الاستهلاك الكلي للطاقة بنسبة 35-40%.
● عائد الاستثمار: يتم تقصير فترة استرداد استثمار المشروع إلى 3-4 سنوات فقط.
● نقاء المنتج: يمكنه إنتاج منتجات بتركيز يتجاوز 90% بشكل مستقر، مما يلبي الطلب في الأسواق الرفيعة المستوى.
● التكاليف التشغيلية: يقلل درجة عالية من الأتمتة من تكاليف العمالة بنسبة 50%.
ثالثاً: تطبيقات متنوعة لحمض الفورميك: من الصناعات التقليدية إلى المجالات الناشئة
باعتباره مادة خام كيميائية عضوية مهمة، يتمتع حمض الفورميك بمجموعة واسعة جداً من مجالات التطبيق.
المجالات التقليدية للتطبيق
● صناعة الأعلاف الحيوانية: يمكن إضافة حمض الفورميك إلى العلف المخمر لمنع نمو العفن والبكتيريا، ومنع فساد العلف، وتحسين جودة العلف. وفي قطاع مضافات الأعلاف، تشهد تطبيقات حمض الفورميك وأملاحه (مثل فورمات الكالسيوم وفورمات البوتاسيوم) أسرع نمو.
● صناعة الجلود: تُستخدم حمض الفورميك كعامل إزالة الجير وعامل دبغ في عملية دبغ الجلود. ويساعد على اختراق أملاح الكروميوم وتثبيتها بشكل أفضل داخل ألياف الجلد، مما يحسن من جودة الجلد.
● صباغة النسيج: يُستخدم كعامل اختزال حمضي لتبييض قبعات القش والجلود، ويمكنه إزالة بقع الحبر والصدأ من الملابس. وبعد الصباغة، يُستخدم لمعادلة القلويات المتبقية وتثبيت ألوان الصبغة.
● صناعة المطاط: بصفته عامل تجلط لمطاط اللاتكس الطبيعي، فإنه يتسبب في تجلط مطاط اللاتكس ليصبح مطاطًا خامًا، مما يحسن جودة المطاط الطبيعي.
التصنيع الكيميائي: يُستخدم في تصنيع مجموعة متنوعة من أملاح الفورمات وأسترات الفورمات، وكذلك الوسائط المستخدمة في الأدوية والمبيدات.
مجالات تطبيق ناشئة
● المنظفات الصديقة للبيئة: تتميز حمض الفورميك بحمضية معتدلة، وقابلية عالية للتحلل البيولوجي، كما أنه أقل تآكلاً بشكل كبير مقارنة بالأحماض غير العضوية مثل حمض الهيدروكلوريك وحمض الكبريتيك. ويُستخدم على نطاق واسع في تطوير عوامل تنظيف صناعية صديقة للبيئة وعوامل إزالة الترسبات.
● ناقل طاقة الهيدروجين: يحتوي حمض الفورميك على نسبة عالية من الهيدروجين (4.4٪ وزناً). وبفعل عامل محفز، يمكن أن يتفكك لإنتاج هيدروجين عالي النقاء، مما يجعله ناقلاً محتملاً لطاقة الهيدروجين، ويوفّر مصدر هيدروجين للخلايا الوقودية.
● معالجة أسطح المعادن: يمكن لحمض الفورميك ومحاليله المائية أن يذيبا العديد من المعادن وأكاسيدها وهيدروكسيداتها وأملاحها. وجميع أملاح الفورمات الناتجة تكون قابلة للذوبان في الماء، ما يجعله مناسباً كعامل تنظيف كيميائي. وبما أن حمض الفورميك خالٍ من أيونات الكلوريد، فإنه يمكن استخدامه في تنظيف المعدات التي تحتوي على مكونات من الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ.
رابعاً: المشهد العالمي لسوق حمض الفورميك
قدرة إنتاج مركزّة للغاية
وفقًا لأحدث بيانات الصناعة، فإن القدرة العالمية على إنتاج حمض الفورميك مركزّة بشكل كبير. حيث تمثل الصين 53٪ من الطاقة الإجمالية العالمية، ما يجعلها القوة المهيمنة المطلقة في إمدادات حمض الفورميك عالميًا. ويؤدي هذا التركز العالي للإنتاج إلى مخاطر في سلسلة التوريد، ولكنه يُعد أيضًا فرصة استراتيجية للمناطق الأخرى لبناء قدرات إنتاج محلية.

نمو قوي ومتنوع في الطلب
باعتباره مادة خام كيميائية عضوية مهمة، تستمر مجالات تطبيق حمض الفورميك في التوسع:
● صناعة الأعلاف الحيوانية: وهي أكبر قطاع تطبيقي عالميًا، وتشكل 34٪ من إجمالي الاستهلاك. ويستمر نمو الطلب على حمض الفورميك وأملاحه بوصفها مواد حافظة فعالة وبديلًا للمضادات الحيوية في الأعلاف.
● صناعة الجلود: وتشكل 24٪، وهي ضرورية في عمليات إزالة الجير والدباغة.
● صباغة النسيج: بوصفه عامل اختزال حمضي صديق للبيئة، فهو يمتلك حصة سوقية بنسبة 15٪.
● تطبيقات ناشئة: تُظهر مجالات مثل تجلط المطاط، والمنظفات الصديقة للبيئة، وناقلات طاقة الهيدروجين إمكانات كبيرة.
من منظور هيكل الاستهلاك، تعد صناعتا الأعلاف الحيوانية والجلود هما أكثر منطقتين تطبيقيتين هيمنتين على حمض الفورميك، حيث تمثلان معًا أكثر من نصف السوق الكلي.

فجوة العرض والطلب المستمرة والمتزايدة
تشهد اقتصادات نامية مثل الهند، وفيتنام، وتركيا، والبرازيل، وروسيا نموًا سريعًا في الطلب على حمض الفورميك. ومع ذلك، تعاني هذه المناطق من نقص حاد في الطاقة الإنتاجية المحلية. في عام 2024، بلغ حجم حمض الفورميك الذي استوردته هذه الدول الخمس فقط من الصين أكثر من 30٪ من إجمالي صادرات الصين، مما يبرز عدم التوازن الشديد في هيكل العرض والطلب العالمي.
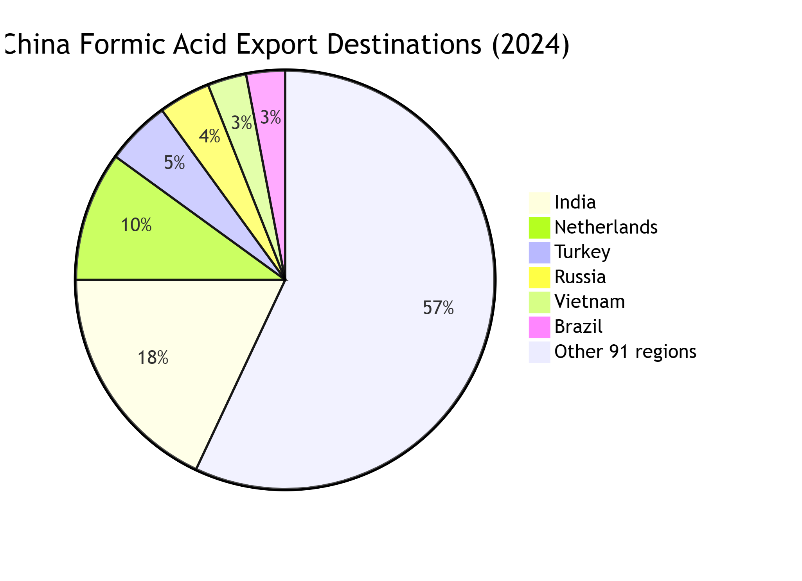
خامسًا. حالة السوق والاتجاهات المستقبلية
نمو سوق مستقر
واصل سوق حمض الفورميك العالمي نموه المستقر في عام 2024. وبلغ حجم السوق العالمي 4.6 مليار يوان صيني في عام 2024، ومن المتوقع أن يتجاوز 5.3 مليار يوان صيني بحلول عام 2029، مما يمثل معدل نمو سنوي مركب (CAGR) بنسبة 3.1٪ من عام 2024 إلى عام 2029. وفي الصين، بلغ حجم السوق 2.216 مليار يوان صيني في عام 2024، ومن المتوقع أن يتجاوز 3 مليارات يوان صيني في عام 2025.
تُعد منطقة آسيا والمحيط الهادئ أكبر سوق لحمض الفورميك على مستوى العالم. وفقًا للتحليلات الصادرة عن Report Hall، استحوذت المنطقة على حصة قدرها 49.1٪ من السوق العالمية في عام 2023، مدفوعة بشكل أساسي بالنشاط الزراعي القوي، ونمو الطلب في صناعات الجلود والمنسوجات، إضافةً إلى التطور في القطاعات الدوائية والكيميائية. وتشمل الأسواق المهمة الأخرى أوروبا والأمريكتين.
اتجاهات التطوير المستقبلية
التحديث الصناعي: تؤدي السياسات البيئية الصارمة إلى اعتماد تقنيات إنتاج أنظف. ومن المتوقع أن تتجاوز نسبة الامتثال للصناعة للمعايير البيئية 95٪ بحلول عام 2025. وفي الوقت نفسه، ستعزز الشركات من استثماراتها في البحث والتطوير لمُحفِّزات جديدة وأنظمة تحكم ذكية بهدف خفض تكاليف الإنتاج وزيادة القيمة المضافة للمنتجات.
توسيع مجال التطبيق: باعتباره مادة كيميائية صديقة للبيئة، يتحلل حمض الفورميك إلى ثاني أكسيد الكربون والماء بعد الاستخدام، ولا يتسبب في تلوث مستمر. ومع ارتفاع المتطلبات البيئية العالمية، تظل آفاق استخدامه واعدة في قطاعات مثل الأعلاف (بديلًا للمضادات الحيوية)، والجلود، والصباغة.
التوسع الدولي: ستستكشف الشركات المحلية الأسواق الدولية من خلال التعاون في مجالات الطاقة التصدير التكنولوجي، مع التركيز بشكل خاص على الأسواق الناشئة في جنوب شرق آسيا وأفريقيا.
الحماية البيئية والتصنيع عالي الجودة: تُستخدم حمض الفورميك تدريجيًا بدلًا من الأحماض غير العضوية مثل حمض الهيدروكلوريك وحمض الكبريتيك في مجال المنظفات الصناعية الصديقة للبيئة. وفي الوقت نفسه، تشهد أفران الفراغ متعددة الحجرات التي تستخدم حمض الفورميك، باعتبارها معدات متقدمة للعلاج الحراري، تطبيقات متزايدة في قطاعات رفيعة المستوى مثل تصنيع أجهزة أشباه الموصلات، والخلايا الشمسية، وتحميص المواد السيراميكية. ومن المتوقع أن ينمو مبيعاتها في السوق العالمية بمعدل نمو سنوي مركب قدره 5.1٪ خلال الفترة 2025-2031.
قطاع الطاقة: تلقى التكنولوجيا التي تستخدم حمض الفورميك كناقل محتمل للطاقة الهيدروجينية اهتمامًا متزايدًا. حيث يمكن أن يتفكك هذا الحمض تحت التحفيز لإنتاج هيدروجين عالي النقاء، ليكون مصدرًا للهيدروجين في خلايا الوقود. وتجري حاليًا جهود بحثية وتطويرية ذات صلة.
توصيات استراتيجية
التطبيقات الناشئة التي تدفع النمو
تتسارع تطبيقات حمض الفورميك في مجالات رفيعة المستوى مثل تخزين الهيدروجين، وتصنيع أشباه الموصلات، والمركبات الوسيطة الصيدلانية. وسيؤدي البدء المبكر في هذه المجالات سريعة النمو إلى تحقيق عوائد زائدة للمستثمرين.
الاقتصاد الهيدروجيني: حمض الفورميك، بوصفه ناقلًا آمنًا وفعالًا للهيدروجين، يمتلك إمكانات سوقية هائلة في مجال الطاقة الموزعة.
الكيمياء الخضراء: أصبحت الطرق القائمة على المواد البيولوجية لإنتاج حمض الفورميك أكثر نضجًا بشكل متزايد، بما يتماشى مع اتجاهات التنمية المستدامة.
نصيحة الاستثمار
استنادًا إلى تحليل متعمق لسوق حمض الفورميك العالمي، نقدم التوصيات التالية للمستثمرين المحتملين:
اختيار المنطقة: يُفضل التركيز على الأسواق الناشئة التي تعاني من نقص في القدرة المحلية ونمو سريع في الطلب، مثل جنوب شرق آسيا، وجنوب آسيا، وأمريكا اللاتينية.
مسار التكنولوجيا: اعتماد طريقة ميثيل فورمات الناضجة والموثوقة لضمان قدرة المشروع التنافسية وربحه.
تخطيط السعة: تحديد سعة أولية معقولة بناءً على حجم السوق المستهدف، ويُقترح أن تكون في البداية من 30,000 إلى 50,000 طن/سنة.
استراتيجية التمايز: النظر في التركيز على حمض الفورميك عالي النقاوة أو منتجات محددة لاحقة للإنتاج تجنباً للمنافسة المتجانسة.
المزايا الأساسية للاستثمار في مشاريع إنتاج حمض الفورميك
طلب سوقي مضمون
من المتوقع أن يتوسع سوق حمض الفورميك العالمي بشكل ثابت بمعدل نمو سنوي مركب قدره 3.1٪، ليتجاوز 5.3 مليار يوان صيني بحلول عام 2029. وبالتالي فإن الاستثمار في خط إنتاج حمض الفورميك يستند إلى أساس واضح من الطلب السوقي، خاصةً في المناطق التي تعاني من نقص في الإمدادات المحلية.
دعم سياساتي مواتٍ
إن التشريعات البيئية الصارمة في جميع أنحاء العالم تقود الطلب على الاستبدال بحمض الفورميك في قطاعات الأعلاف والجلود والمنسوجات وغيرها. وقد صنفت الاتحاد الأوروبي وأمريكا الشمالية وعدة دول ومناطق في آسيا والمحيط الهادئ حمض الفورميك كمادة كيميائية صديقة للبيئة، مما يدعم استخدامه عبر مختلف الصناعات.
فرص دمج سلسلة الصناعة
يمكن لإنتاج حمض الفورميك أن يخلق تآزرًا مع إنتاج المواد الخام المرتبطة به مثل الميثانول والغاز الصناعي. كما يمكن أن يمتد إلى المنتجات ذات القيمة المضافة العالية مثل أملاح الفورمات وأسترات الفورمات، مما يتيح تخطيط سلسلة صناعية متكاملة ويعزز القدرة التنافسية الشاملة.
ⅶ. الخاتمة
حمض الفورميك، هذا المركب الكيميائي الذي يبدو بسيطًا، له علاقة بسلسلة صناعية واسعة وسوق عالمية. من مصدره في لسعات النمل إلى الإنتاج الصناعي الحديث على نطاق واسع، ومن تصنيع الجلود التقليدي إلى مجالات الطاقة الهيدروجينية الناشئة، يستمر نطاق استخدام حمض الفورميك في التوسع، مما يُظهر نشاطًا قويًا.
في المستقبل، مع تزايد المتطلبات البيئية والتقدم التكنولوجي، ستشهد صناعة حمض الفورميك تحولًا وتطويرًا عميقين. بالنسبة للشركات، فإن تعزيز البحث والتطوير التكنولوجي، وتوسيع التطبيقات المتطورة، وتطوير الأسواق الناشئة—إلى جانب تعزيز مزايا الإنتاج الحالية—سيكون أمرًا بالغ الأهمية لتحقيق التنمية المستدامة. في ظل الاتجاه العالمي نحو الانتقال الأخضر، من المتوقع أن يُظهر هذا المركب الكيميائي الصديق للبيئة، حمض الفورميك، قيمته في مجالات أكثر، مما يفتح إمكانات نمو جديدة.
قم بزيارة موقعنا الرسمي لمعرفة المزيد من التفاصيل حول تقنية عملية إنتاج حمض الفورميك والحصول على تحليل الجدوى الاستثمارية المخصص وحلول تخطيط المشاريع. سيوفر فريق خبرائنا الفنيين دعمًا شاملاً، بدءًا من تخطيط المشروع وتصميم العمليات وحتى توريد المعداتและการشغيل التجريبي.